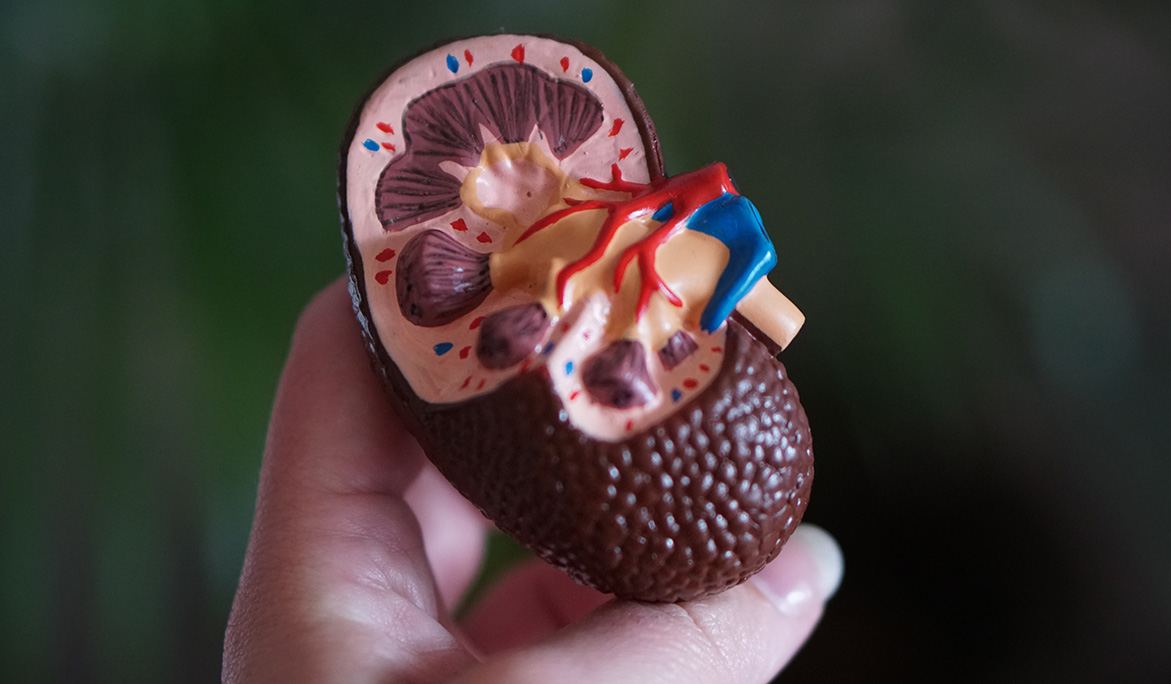
RENAL STONES OR KIDNEY STONES OR NEPHROLITHIASIS
Association : It has association with hypertension, obesity, diabetes and osteoporosis.
Epidemiology : Presents between 20 to 60 years of age. Affects 10% population over lifetime and 75% recurr.
Pathophysiology : Stone growth starts with the formation of crystals in supersaturated urine which then adhere to the urothelium, thus creating the nidus for subsequent stone growth.
- Risk factors :
- Low fluid intake
- Hypercalciuria
- Excess risk of stone formation is seen in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism, deactivating vitamin D receptor (VDR) polymorphisms and activating fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 23 polymorphism.
- Oxalate stones risk factors :
- High salt diet
- Low calcium intake
- Hypocitraturia
- High animal protein intake
- Hyperoxaluria
- Other Symptoms:
- Pink, red or brown urine
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- A persistent need to urinate, urinating more often than usual or urinating in small amounts
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills if an infection is present
- When to see a doctor :
- Pain so severe that you can't sit still or find a comfortable position
- Pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting
- Blood in your urine
- Difficulty passing urine
- Red flag features warranting investigations:
- First stone episode under the age of 25
- Recurrent stones
- Bialateral or multiple stones, nephrocalcinosis
- Strong family history of stones
- PImpaired renal function (eGFR- < 60 ml/min/1.73m2) associated with stones
- Non calcium oxilate stones
- Radioluscent stones (may be urate or cystine)
- stone episode associated with underlying condition (eg: inflammatory bowel disease , gastric byepass suregery or metabolic syndrome)
Initial diagnosis in red flag features patients :
| Sample | Test |
| Serum Sample | Urea, Creatinine, Pottasium, Bicarbonate, Chloride, calcium phosphate, magnesium,25-hydroxyvitamin D,urate |
| Whole blood(EDTA tube) | Parathyroid Hormone |
| Fresh spot urine sample | Urine pH (pH meter better than dipstick) |
| 2 x 24hour urine collection (acidified sample) | Calcium, oxilate, citrate, sodium ( and ceratinine - to assess completeness when comparing repeated 24h collections from the same patient) |
- Types of renal stones
- Calcium stones
- Struvite stones
- Uric acid stones
- Cystine stones
- Management :
- All patients in whom further management is appropriate should receive dietary and lifestyle advice.
- In temperate climates, a fluid intake of at least two litres a day halves recurrence rates.
- A diet high in fruit and vegetables is recommended because the high potassium content promotes urinary citrate excretion
- These foods are also a source of phytates which, like citrate, increase calcium salt solubility.
- An adequate calcium intake, with restricted animal protein, reduces urine oxalate.
- A limited salt and sugar intake is also advised.
- Where possible, an underlying disorder predisposing to stone formation should be identified and treated.
| Urine chemistry risk factor | Possible effect on stone formation | Treatment |
| Hypercalcuria | Most stones contain calcium | Dietary salt and sugar restriction(Thiazide +/- amiloride) |
| Hyperoxeluria NB: urine oxelate often within the 'reference range' in calcium oxelate stone formers | Common component of stones | Dietery restriction of Animal protein and high oxelate foods Adequete diary calcium intake |
| Hyprocitraturia | Reduced solubility of calcium salts | High fruit vegetable intake citrate supplementation |
| Low urine pH | Reduced solubility of calcium oxalate, uric acid and cystine | Urine alkalinization with citrate or bicarbonate ( avoid in calcium phosphate nephrolithiasis) |